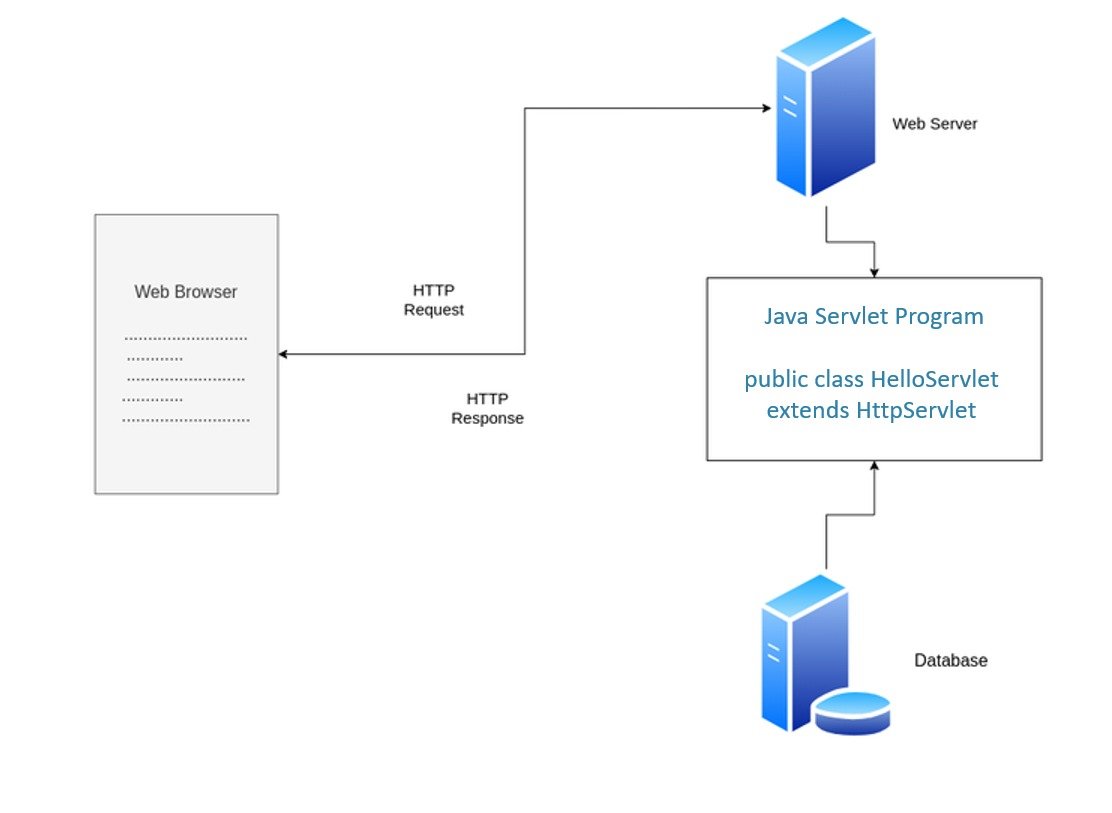
In the world of web development, servlets are like the little helpers that run on a server and respond to requests from web browsers. If you’ve ever clicked a button on a website and seen the page change, there’s a good chance a servlet was involved!
What is a Servlet?
A servlet is a Java program that runs on a server. It handles requests (like clicking a button) and responses (like showing you a new webpage). Think of it as a waiter in a restaurant: you tell the waiter (the servlet) what you want (the request), and the waiter brings you your food (the response).
Your First Servlet Program
Let’s dive into creating a simple servlet that says “Hello, World!” when you visit it.
Step-by-Step Guide
- Set Up Your Environment:
- Java Development Kit (JDK): Make sure you have the JDK installed on your computer.
- Apache Tomcat: This is a popular web server for running servlets. Download and install Apache Tomcat.
- Integrated Development Environment (IDE): Use an IDE like Eclipse or IntelliJ IDEA to write your code.
- Create a New Project:
- Open your IDE and create a new Dynamic Web Project (in Eclipse) or a new Web Application (in IntelliJ IDEA).
- Write Your Servlet Code:
- Create a new Java class in your project. Name it
HelloServlet.java.
- Create a new Java class in your project. Name it
Here’s the code for our first servlet:
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@WebServlet(“/hello”)
public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html");
response.getWriter().println("<h1>Hello, World!</h1>");
}}
Explaining the Code
- Imports: At the top, we import the necessary classes. These classes help our servlet interact with web requests and responses.
- @WebServlet(“/hello”): This line tells the server that this servlet should respond to requests sent to the
/helloURL. - doGet Method: This method handles GET requests. When someone visits the URL
/hello, this method is called.response.setContentType("text/html");: This tells the browser that we are sending back an HTML response.response.getWriter().println("<h1>Hello, World!</h1>");: This sends back a simple HTML message: “Hello, World!”
- Deploy Your Servlet:
- Copy your project to the webapps folder of your Tomcat installation.
- Start Tomcat.
- Access Your Servlet:
- Open your web browser and go to
http://localhost:8080/your_project_name/hello. - You should see the message “Hello, World!” displayed on the page.
- Open your web browser and go to